验证曲线validation_curve
validation_curve()的作用
误差是由偏差(bias)、方差(variance)、噪声(noise)组成。 偏差:模型对于不同的训练样本集,预测结果的平均误差 方差:模型对于不同训练样本集的敏感程度 噪声:数据集本身的一项属性 同样的数据,(cos函数上的点加上噪声),我们用同样的模型(polynomial),但是超参数却不同(degree =1,4,15),会得到不同的拟合效果:
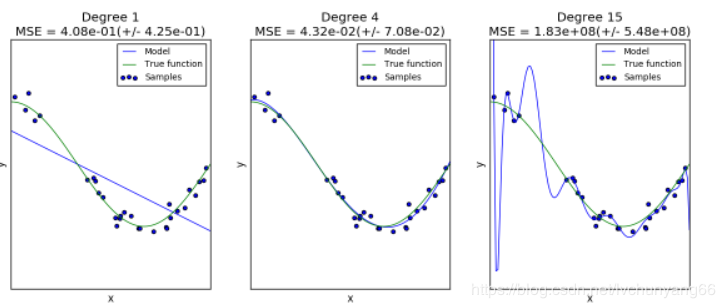
第一个模型太简单,模型本身就拟合不了这些数据(高偏差,underfitting); 第二个模型可以看成几乎完美地拟合了数据; 第三个模型完美拟合了几乎所有的训练数据,但却不能很好的拟合真实的函数,也就是对于不同的训练数据很敏感(高方差,overfitting)。 对于以上第一和第三个模型,我们可以选择模型和超参数来得到效果更好的配置,也就是可以通过验证曲线(validation_curve)来调节。
validation_curve的含义
证曲线(validation_curve)和学习曲线(sklearn.model_selection.learning_curve())的区别是,验证曲线的横轴为某个超参数,如一些树形集成学习算法中的max_depth、min_sample_leaf等等。 从验证曲线上可以看到随着超参数设置的改变,模型可能从欠拟合到合适,再到过拟合的过程,进而选择一个合适的位置,来提高模型的性能。 需要注意的是,如果我们使用验证分数来优化超参数,那么该验证分数是有偏差的,它无法再代表魔心的泛化能力,我们就需要使用其他测试集来重新评估模型的泛化能力。 即一般我们需要把一个数据集分成三部分:train、validation和test,我们使用train训练模型,并通过在 validation数据集上的表现不断修改超参数值(例如svm中的C值,gamma值等),当模型超参数在validation数据集上表现最优时,我们再使用全新的测试集test进行测试,以此来衡量模型的泛化能力。
不过有时画出单个超参数与训练分数和验证分数的关系图,有助于观察该模型在该超参数取值时,是否过拟合或欠拟合的情况发生,如下两个图:
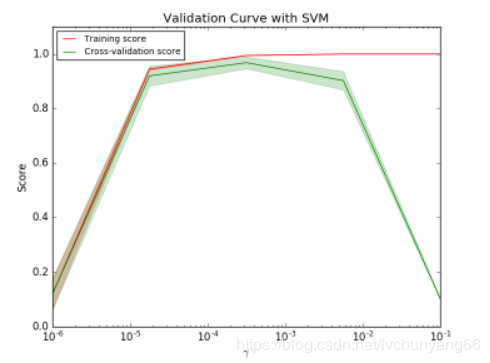
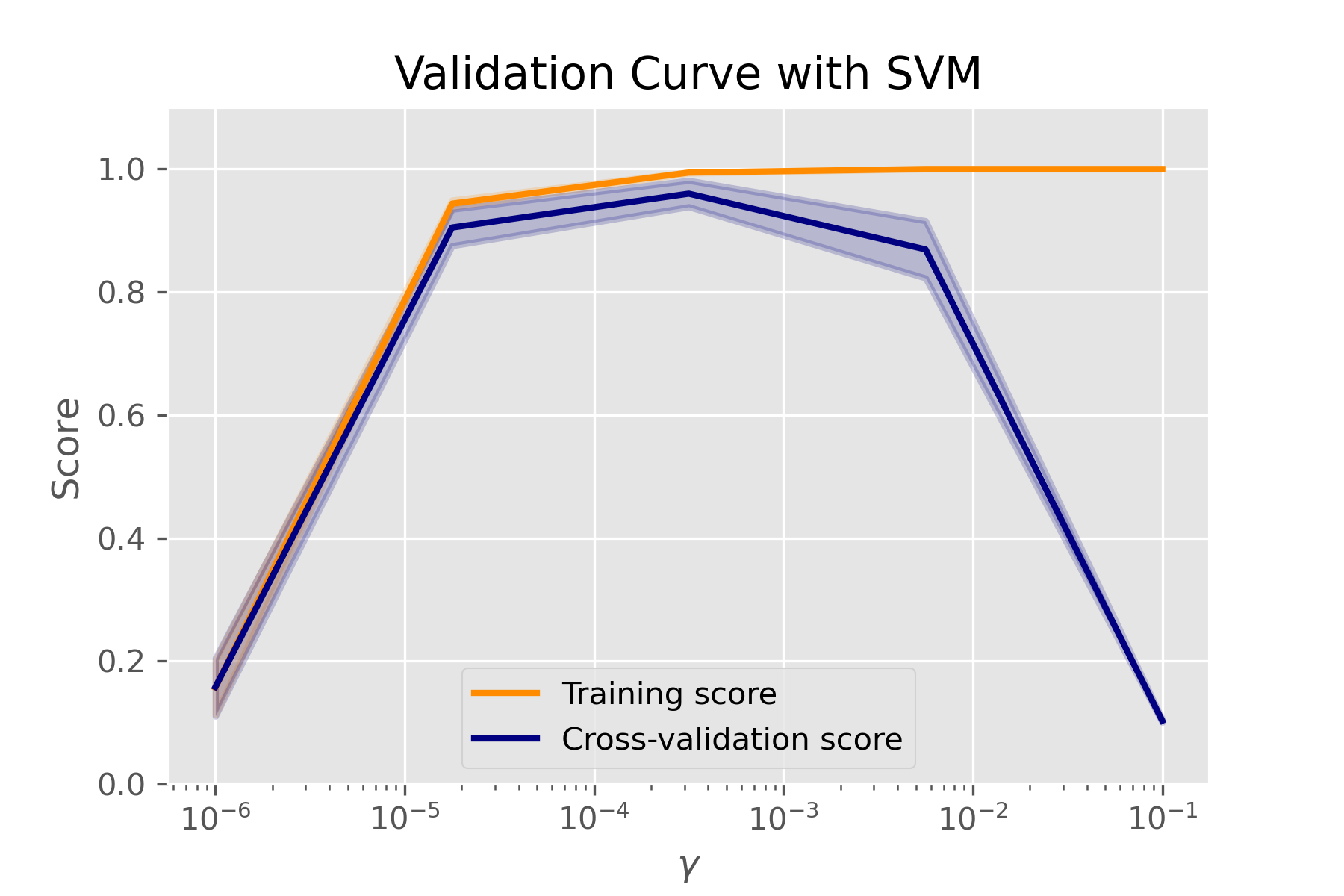
如图是SVM在不同gamma时,它在训练集和交叉验证上的分数: gamma很小时,训练分数和验证分数都很低,为欠拟合; gamma逐渐增加时,两个分数都较高,此时模型相对不错; gamma太高时,训练分数高,验证分数低,学习器会过拟合。 本例中,可以选验证集准确率开始下降,而测试集越来越高那个转折点作为gamma的最优选择。
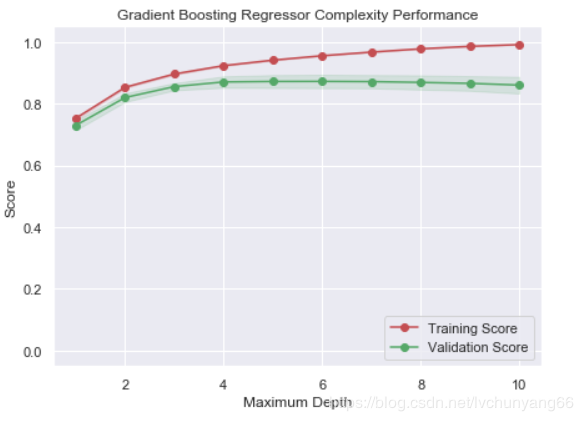
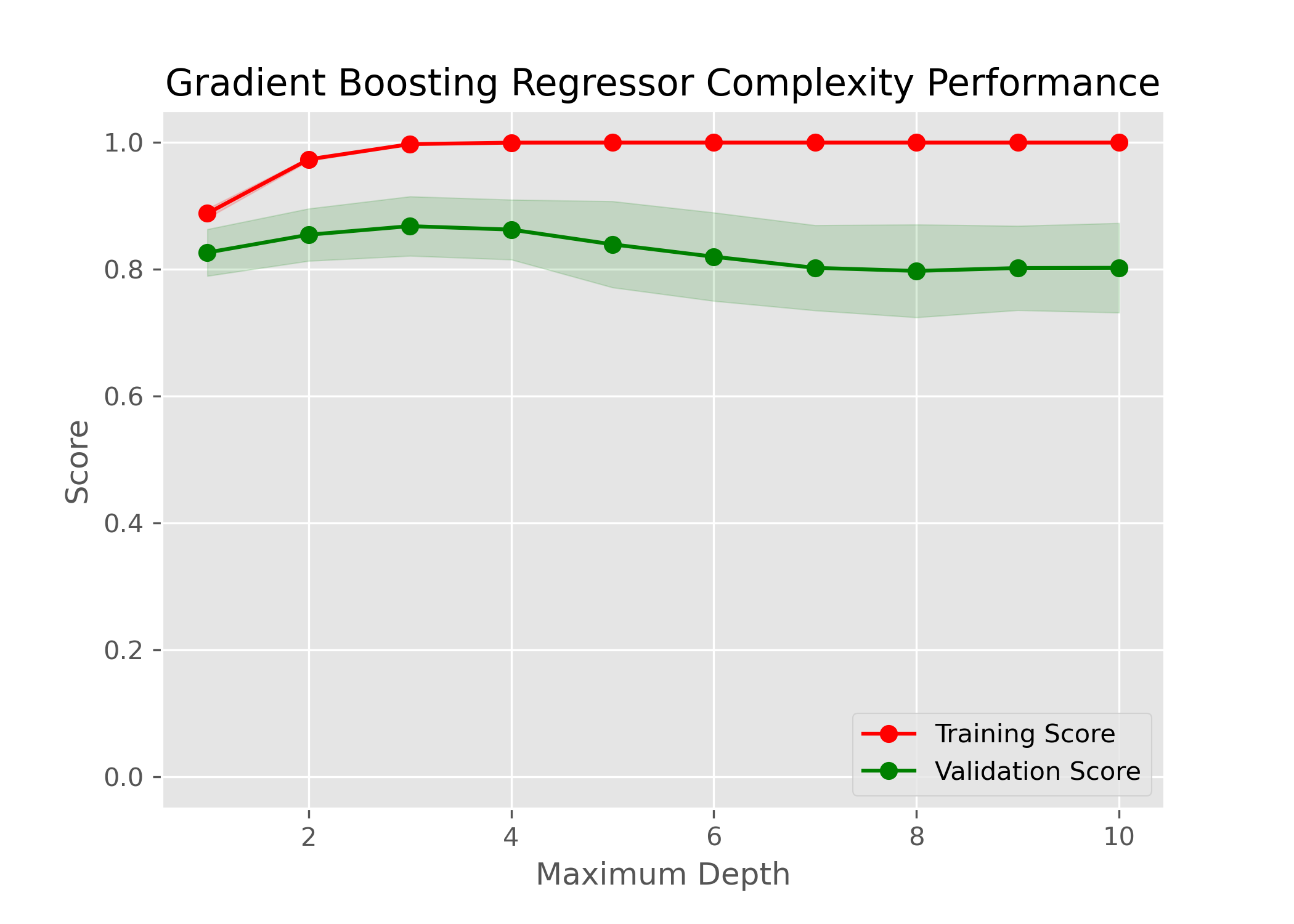
如上图,max_depth的最佳值应该定位5
函数
validation_curve 是展示某个因子,不同取值的算法得分
sklearn.model_selection.validation_curve(estimator,
X, y, *,
param_name,
param_range,
groups=None,
cv=None,
scoring=None,
n_jobs=None,
pre_dispatch='all',
verbose=0,
error_score=nan)
参数
estimator: 评估器X: 训练集y: 训练集对应的标签param_name: str ,要改变的参数的名字,如果当model为SVC时,改变gamma的值,求最好的那个gamma值param_rang: array-like of shape (n_values,) 给定的参数范围cv: 交叉验证生成器或可迭代的,可选的 确定交叉验证拆分策略。cv的可能输入是:None,要使用默认的 5 折交叉验证- int, to specify the number of folds in a
(Stratified)KFold, - CV splitter,
- An iterable yielding (train, test) splits as arrays of indices.
For int/None inputs, if the estimator is a classifier and
yis either binary or multiclass,StratifiedKFoldis used. In all other cases,KFoldis used.scoring: str or callable, default=Non 打分类型,如accuracy,r2等,
返回值:
- train_scores :array of shape (n_ticks, n_cv_folds)
Scores on training sets.
est_scores:array of shape (n_ticks, n_cv_folds) Scores on test set.
案例 1
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import validation_curve
X, y = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
param_range = np.logspace(-6, -1, 5)
train_scores, test_scores = validation_curve(
SVC(), X, y, param_name="gamma", param_range=param_range,
scoring="accuracy", n_jobs=1)
train_scores_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)
train_scores_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)
test_scores_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)
test_scores_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)
plt.title("Validation Curve with SVM")
plt.xlabel(r"$\gamma$")
plt.ylabel("Score")
plt.ylim(0.0, 1.1)
lw = 2
plt.semilogx(param_range, train_scores_mean, label="Training score",
color="darkorange", lw=lw)
plt.fill_between(param_range, train_scores_mean - train_scores_std,
train_scores_mean + train_scores_std, alpha=0.2,
color="darkorange", lw=lw)
plt.semilogx(param_range, test_scores_mean, label="Cross-validation score",
color="navy", lw=lw)
plt.fill_between(param_range, test_scores_mean - test_scores_std,
test_scores_mean + test_scores_std, alpha=0.2,
color="navy", lw=lw)
plt.legend(loc="best")
案例 2
带有 cv 参数
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from time import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
from sklearn.model_selection import validation_curve
def ModelComplexity(X, y):
""" Calculates the performance of the model as model complexity increases.
The learning and testing errors rates are then plotted. """
# Create 10 cross-validation sets for training and testing
cv = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# Vary the max_depth parameter from 1 to 10
max_depth = np.arange(1, 11)
start = time()
# Calculate the training and testing scores
train_scores, test_scores = validation_curve(GradientBoostingRegressor(), X, y,
param_name="max_depth",
param_range=max_depth,
cv=cv,
scoring='r2')
print(time()-start)
# Find the mean and standard deviation for smoothing
train_mean = np.mean(train_scores, axis=1)
train_std = np.std(train_scores, axis=1)
test_mean = np.mean(test_scores, axis=1)
test_std = np.std(test_scores, axis=1)
# Plot the validation curve
plt.figure(figsize=(7, 5))
plt.title('Gradient Boosting Regressor Complexity Performance')
plt.plot(max_depth, train_mean, 'o-', color='r', label='Training Score')
plt.plot(max_depth, test_mean, 'o-', color='g', label='Validation Score')
plt.fill_between(max_depth, train_mean - train_std,
train_mean + train_std, alpha=0.15, color='r')
plt.fill_between(max_depth, test_mean - test_std,
test_mean + test_std, alpha=0.15, color='g')
# Visual aesthetics
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.xlabel('Maximum Depth')
plt.ylabel('Score')
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
ModelComplexity(X_train, y_train)
画图时,横轴为 param_range,纵轴为 scoreing: