最小二乘法函数拟合leastsq
最小二乘估计原理是这样的: 其中 ε 独立同分布。 非线性最小二乘法中,SST=SSR+SSE不再成立,但仍然可以定义R_squared=1-SSE/SST
leastsq可以用来做最小二乘估计,可以在线性拟合和非线性拟合中使用。
leastsq
scipy.optimize.leastsq(func,
x0, args=(),
Dfun=None, full_output=0,
col_deriv=0, ftol=1.49012e-08,
xtol=1.49012e-08, gtol=0.0,
maxfev=0, epsfcn=None,
factor=100, diag=None)
参数:
一般我们只要指定前三个参数就可以了:
func:是我们自己定义的一个计算误差的函数,x0:是计算的初始参数值args:tuple, optional 是指定func的其他参数,都放在这个元组中
func:是个可调用对象,给出每次拟合的残差。最开始的参数是待优化参数;后面的参数由args给出x0:初始迭代值args:一个元组,用于给func提供额外的参数。Dfun:用于计算func的雅可比矩阵(按行排列)。默认情况下,算法自动推算。它给出残差的梯度。最开始的参数是待优化参数;后面的参数由args给出full_output:如果非零,则给出更详细的输出col_deriv:如果非零,则计算雅可比矩阵更快(按列求导)ftol:指定相对的均方误差的阈值xtol:指定参数解收敛的阈值gtol:Orthogonality desired between the function vector and the columns of the Jacobianmaxfev:设定算法迭代的最大次数。如果为零:如果为提供了Dfun,则为100*(N+1),N为x0的长度;如果未提供Dfun,则为200*(N+1)epsfcn:采用前向差分算法求解雅可比矩阵时的步长。factor:它决定了初始的步长diag:它给出了每个变量的缩放因子
返回值:
x:拟合解组成的数组cov_x:Uses the fjac and ipvt optional outputs to construct an estimate of the jacobian around the solutioninfodict:给出了可选的输出。它是个字典,其中的键有:nfev:func调用次数fvec:最终的func输出fjac:A permutation of the R matrix of a QR factorization of the final approximate Jacobian matrix, stored column wise.ipvt:An integer array of length N which defines a permutation matrix, p, such that fjacp = qr, where r is upper triangular with diagonal elements of nonincreasing magnitude
ier:一个整数标记。如果为 1/2/3/4,则表示拟合成功mesg:一个字符串。如果解未找到,则它给出详细信息
基本使用
线性拟合
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
# 样本数据(Xi,Yi),需要转换成数组(列表)形式
Xi = np.array([160, 165, 158, 172, 159, 176, 160, 162, 171])
Yi = np.array([58, 63, 57, 65, 62, 66, 58, 59, 62])
定义残差并寻优:
# 需要拟合的函数func :指定函数的形状 k= 0.42116973935 b= -8.28830260655
def func(p, x):
k, b = p
return k*x+b
# 偏差函数:x,y都是列表:这里的x,y更上面的Xi,Yi中是一一对应的
def error(p, x, y):
return func(p, x)-y
给定初始值,进行拟合
# k,b的初始值,可以任意设定,经过几次试验,发现p0的值会影响cost的值:Para[1]
p0 = [1, 20]
# 把error函数中除了p0以外的参数打包到args中(使用要求)
Para = leastsq(error, p0, args=(Xi, Yi))
读取结果:
# 读取结果
k, b = Para[0]
print("k=", k, "b=", b)
计算误差:
残差平方和
def S(k,b):
error=np.zeros(k.shape)
for x,y in zip(X,Y):
error+=(y-(k*x+b))**2
return error
S(k,b)
# array(405808.61964307)
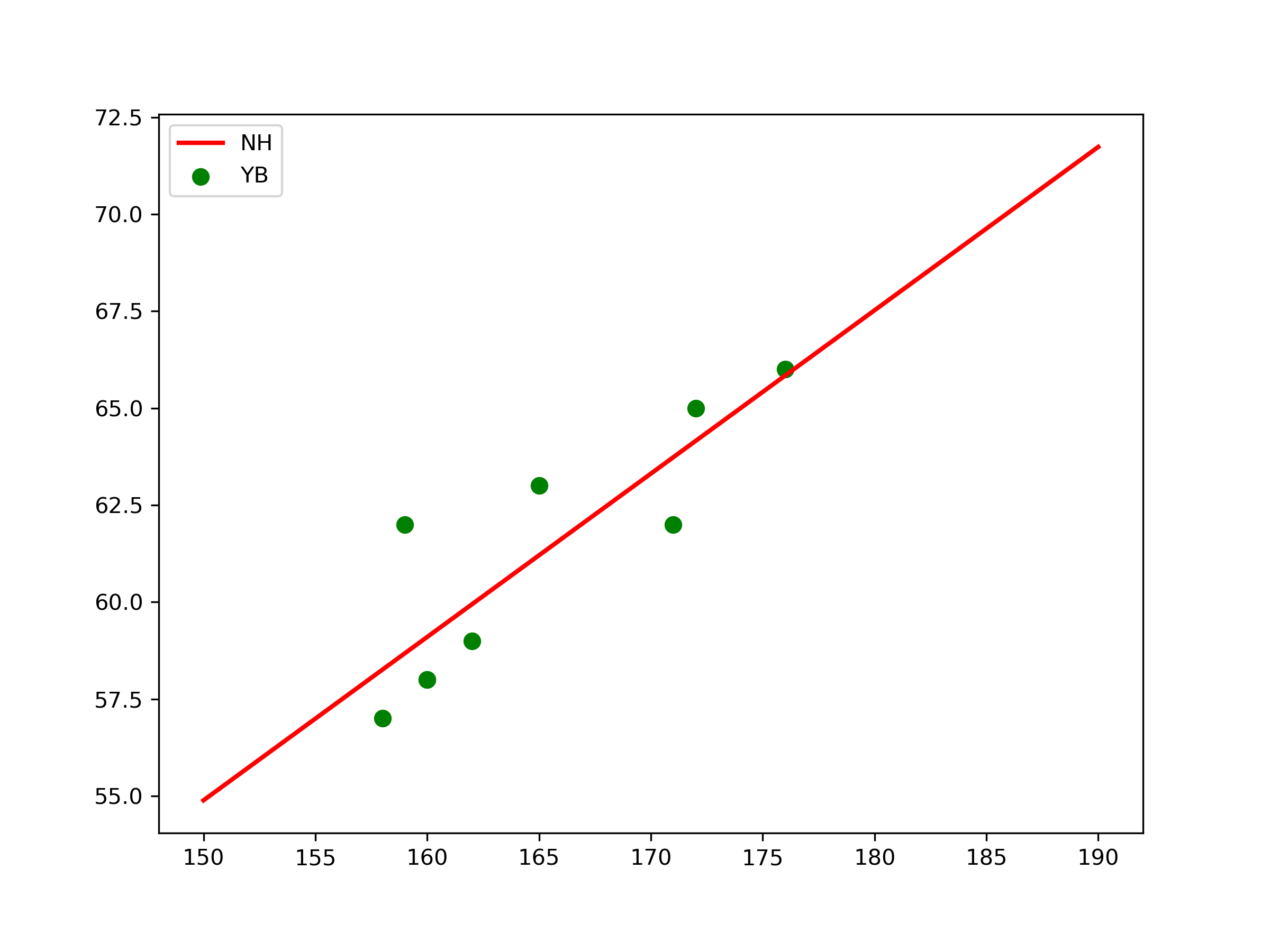
可视化:
# 画样本点
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) # 指定图像比例: 8:6
plt.scatter(Xi, Yi, color="green", label="YB", linewidth=2)
# 画拟合直线
x = np.linspace(150, 190, 100) # 在150-190直接画100个连续点
y = k*x+b # 函数式
plt.plot(x, y, color="red", label="NH", linewidth=2)
plt.legend() # 绘制图例
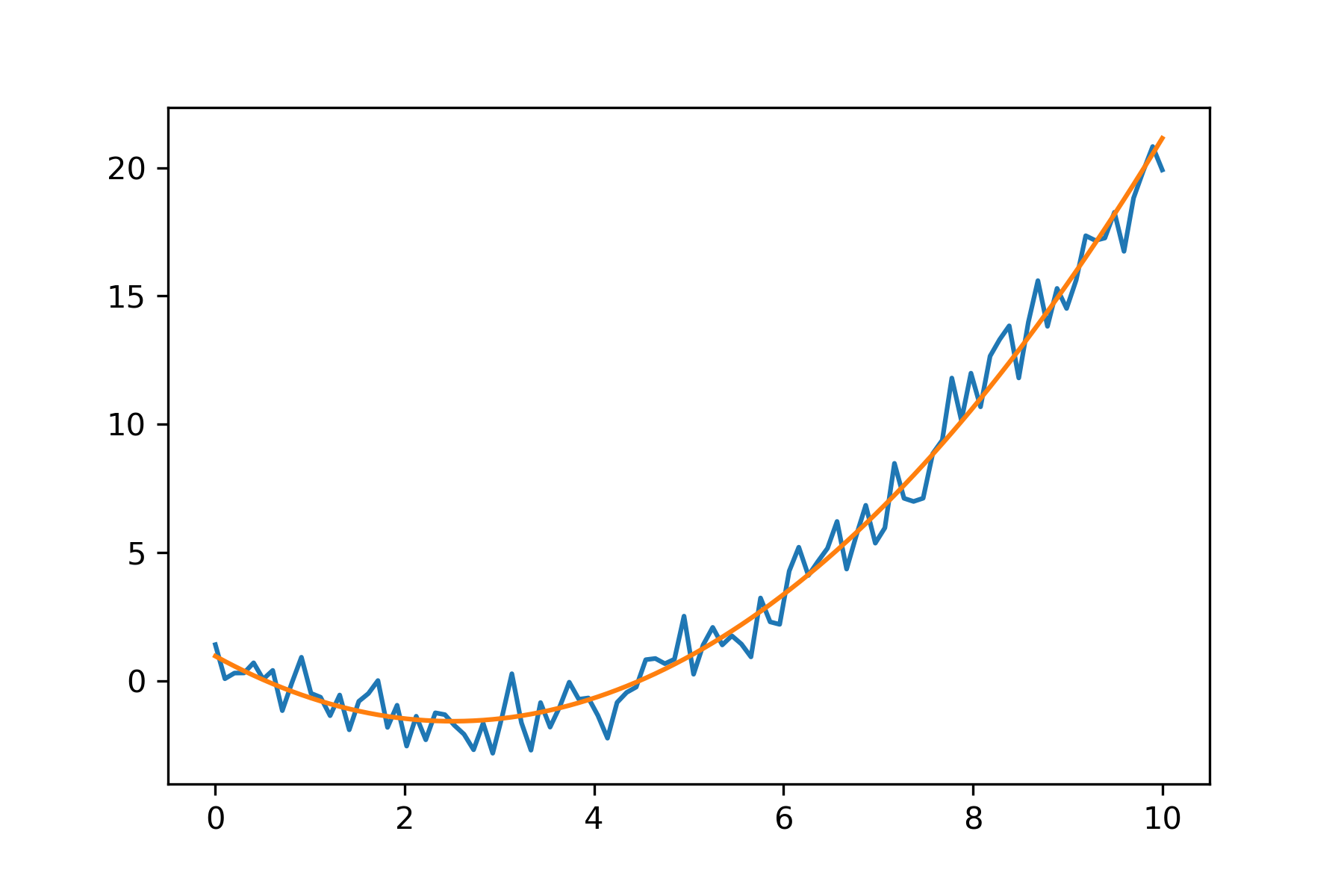
曲线拟合
定义目标函数,准备一一检验其拟合效果
# 目标函数
def test_func(x, p):
a, b, c = p
return a*x**2+b*x+c
# 残差
def residuals(p,y,x):
return y-test_func(x,p)
生成模拟数据
p_true = [0.4, -2, 0.9] # 真实值
X = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y = test_func(X, p_true)+np.random.randn(len(X))
拟合
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
# 先验的估计,真实数据分析流程中,先预估一个接近的值。这里为了测试效果,先验设定为 1
p_prior = np.ones_like(p_true)
plsq = leastsq(residuals, p_prior, args=(y, X))
print(p_true)
print(plsq)
[0.4, -2, 0.9]
(array([ 0.40067724, -1.99507171, 0.86224339]), 3)
画图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(X, y)
plt.plot(X, test_func(X, plsq[0]))